When it comes to K-12 WiFi networks in this country, over half lack the proper infrastructure needed to support the necessary technology for today's digital learning environment.
Luckily, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC), has been trying to solve this major problem since the mid-90s by helping schools and libraries obtain more affordable broadband through a program called E-Rate. This program, along with the entirety of accessing affordable communication services, is administrated by an independent, not-for-profit corporation called the Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC).
In 2017, 79 percent of school districts and libraries reported that they have faster internet connections thanks to E-rate. This translates to helping about 40 million students across the United States get reliable access to WiFi.
When it comes to funding your wireless network upgrades it’s never easy, and although the E-rate program offers a valuable solution, it isn’t exactly the easiest process.
Before you apply it’s important to have a firm grasp of what the E-rate is, who is eligible and what exactly can be funded under the program. We have outlined the E-rate program with the information that you should know before you get started in the application process.
What is E-rate?
E-rate is a government program that offers reduced rates or discounts on internet access, internal connections, and managed WiFi to both schools and libraries - thisincludes the maintenance to those systems as well.
What Types of Wireless Equipment can be Funded?
Other than who is eligible for the program, what is covered by E-rate is probably the most important question schools have. What gets funded is split into two different categories: Category One and Category Two.
Category One: covers broadband services which brings internet access into the building though Internet Service Providers (ISPs)
Category Two: focuses on internal connections, managed internal broadband services, and the basic maintenance of internal connections
For the purposes of this blog, we’ll be focusing on Category Two a.k.a. the WiFi side of things.
Internal Connections
An “Internal Connection” is just the hardware that’s needed, such as the cabling and equipment, in order to transport the digital information into the classrooms.
Category Two Eligible “Internal Connections” Components List:
-
Antennas, connectors, and related components used for internalbroadband connections
-
Cabling
-
Caching
-
Firewalls used to ensure the continued operation of eligibleequipment by protecting equipment from security hazards
-
Racks that support eligible internal connections components
-
Routers
-
Network switches
-
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS)/Battery Backupnecessary for basic power protection for eligible equipment
-
Access points used in a Local Area Network (LAN) or a WirelessLocal Area Network (WLAN) environment – i.e. wireless access points
-
Wireless Controller Systems
-
Software necessary to support this list of eligible broadbandinternal connections components, including Client Access
USAC’s Glossary of Eligible Service List here
**Important Note: The FCC’s official Eligible Service List (ESL) for the 2020 funding year will not be available until sometime in the fall of 2019, so these services and other details may change.
Managed Internal Broadband Services (MIBS)
The Category Two E-rate program also includes what USAC refers to as “Managed Internal Broadband Services (MIBS),” but it is also known as Managed WiFi or Managed Wireless Network Services to the rest of the world.
"Managed WiFi"is when a school purchases all the WiFi and networking hardware upfront and then bundles professional services (advanced software and managed network services) on a subscription basis.
If you do apply for E-rate, the money that you would receive for your school is only available for 5 years and then it essentially disappears. Due to that small catch, many school districts were being advised to use all their money at one time on hardware. This created its own problems (especially for schools that had a small or inexperienced IT team), because they had a bunch of the hardware (internal connections), but no one to manage the network. That’s why it is important, if your school doesn’t have the necessary internal resources to manage your network, to apply for E-rate using MIBs.
Basic Maintenance
For the most part, “Basic Maintenance” is self-explanatory, in that in encumbers the repair and replacment of devices or connections. What is unique in E-rate’s situation is that basic maintenance also includes upkeep services, technical support, and configuration changes!
Category Two “Basic Maintenance” List Now Includes:
- Repair and upkeep of eligible hardware
- Wire and cable maintenance
- Configuration changes
- Basic technical support including online and telephone basedtechnical support
- Software upgrades and patches including bug fixes andsecurity patches
- It needs to be stated that all of the above is due for comment and further clarification from the FCC, so be sure to check with the USAC and/or FCC for the latest information.
Who is Eligible for the E-rate Program?
The E-rate program is available to all public and most non-profit K-12 schools, as well as both public and private libraries.
They can apply for this program through different entities, such as by:
- Individual School or Library
- School District or Library System
- Statewide (Consortium) of Libraries or Schools
Other types of entities that this program covers include pre-kindergarten, juvenile justices, adult educations, and non-instructional facilities.
What discounts are provided under E-rate?
The discounts for eligible services under Category Two range from 20 to 85 percent of the money spent purchasing a new school wireless network.
The percent of eligibility primarily depends on the percent of students eligible for free and reduced lunches under the National School Lunch Program (NSLP), as well as the location of the facility – either in a urban or rural environment.
With the information from the 2019 Funding Year, here’s an example of how the discounts would work:
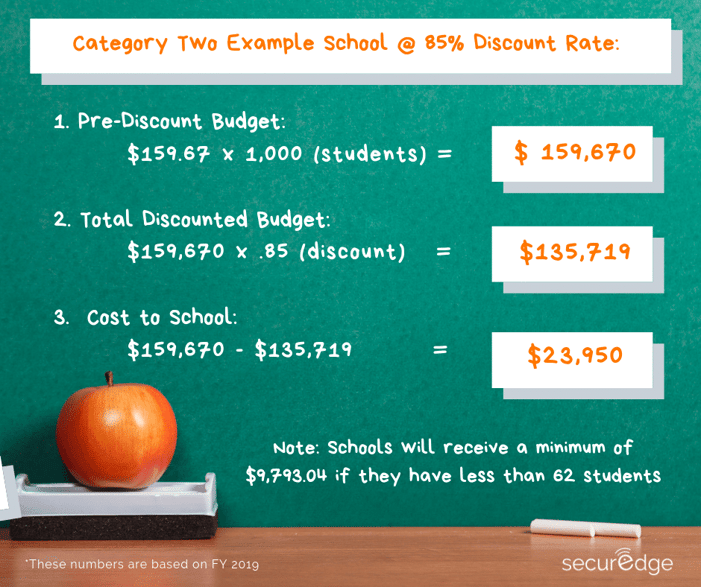
Data retrieved from USAC's Category Two Budget
Keep in mind that these numbers are based on federal funding from the FCC. In many cases, your state might offer additional funding to cover the cost to the school through a separate state contract.
When it comes to bringing the latest wireless technology into your school, utilizing the E-rate program should be on the top of your to-do list.
When you crunch the numbers for your own school, you will find that going through the the E-rate process is well-worth it – especially for the students.
If you are interested in more information about getting a wireless network design your school, we are here to help! SecurEdge is an E-rate service provider and has deployed hundreds of networks for K-12 schools across the nation.
With applications currently being accepted for Funding Year 2020, E-rate just might be the best the way to finally close the technology gap.
Coming Soon: Since the FCC allows for feedback, it improves the E-rate’s budget approach and lets everyone know of the new changes through its Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM). We’ve been hearing a lot of exciting changes that are being proposed for the upcoming FY2020 and many of these changes will have a tremendous, positive impact on the way schools get their hardware and wireless networks. Stay tuned!
*Editor's note: This blog post was originally posted in August 2014 and has been completely revamped and updated for accuracy and helpfulness.






